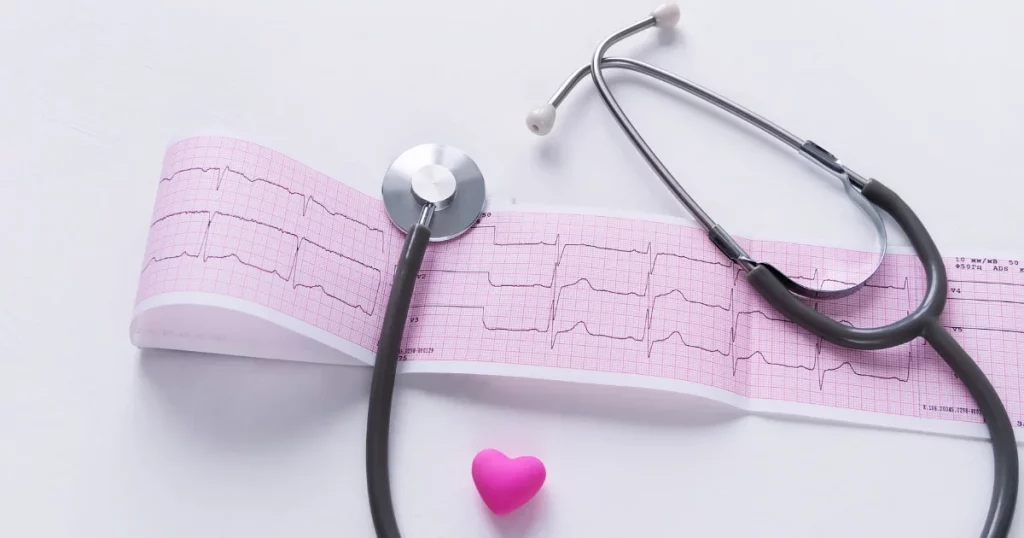
Imagine a scenario where someone experiences chest pain and shortness of breath, prompting a visit to the doctor. In this critical moment, a simple yet powerful tool comes into play – the Electrocardiogram (ECG). At the heart of every ECG, quite literally, is the ECG paper. Electrocardiogram (ECG) tests play a crucial role in understanding heart health. One essential component of this process is the ECG paper. This guide aims to demystify the ECG paper, exploring its features, compatibility, and best practices. Please note that this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Table of Contents
Understanding ECG Technology
At the core of the heart’s functionality lies an intricate electrical conduction system, that orchestrates the rhythm of each heartbeat. The journey begins in the sinoatrial (SA) node, often referred to as the heart’s natural pacemaker. From here, electrical impulses travel through the atria, prompting them to contract and propel blood into the ventricles.
This electrical journey continues through the atrioventricular (AV) node, slowing down momentarily to allow the ventricles to fill completely. The impulses then travel along specialized pathways, known as the Bundle of His and Purkinje fibers, stimulating the ventricles to contract and pump blood to the rest of the body. This orchestrated sequence of electrical events ensures the synchronized and efficient functioning of the heart.
The Role of ECGs: Capturing and Displaying the Electrical Signals
Now, imagine if we could capture and visualize these electrical signals to gain insights into the heart’s performance. That’s precisely what an ECG does. Electrocardiograms record the electrical activity of the heart and transform it into a visual representation – the familiar ECG waveform.
ECG paper serves as the canvas for this representation. The paper features a grid that measures time along the horizontal axis and voltage along the vertical axis. As the heart’s electrical impulses are detected by electrodes placed on the skin, the ECG machine translates these signals onto the paper, creating a waveform. Each wave corresponds to a specific phase of the heart’s activity – the P wave represents atrial depolarization, the QRS complex signifies ventricular depolarization, and the T wave indicates ventricular repolarization.
In essence, ECG paper captures the nuances of the heart’s electrical symphony, providing healthcare professionals with a visual guide to identify irregularities, diagnose conditions, and tailor interventions accordingly.
Also read: Utilizing Immuno-Chemistry Analyzers for Advanced Testing
Unveiling ECG Paper
In the world of cardiac diagnostics, ECG paper emerges as the unassuming yet indispensable canvas that captures the intricate dance of the heart’s electrical signals. Let’s delve into the purpose, material, and key features that make ECG paper an essential component in unraveling the mysteries of cardiac health.
Understanding the Purpose: Recording ECG Tracings for Analysis
The primary purpose of ECG paper is to serve as a receptive medium for recording the electrical signals generated by the heart. As the heart beats, electrical impulses are detected by electrodes attached to the skin, and these signals are then translated into visual tracings on the ECG paper. This visual representation, often seen as the familiar waveform, provides healthcare professionals with a tangible record for analysis and interpretation.
Material: Thermal Paper and Its Responsive Nature
ECG paper is predominantly made from thermal paper, a unique material that responds to heat. This characteristic is particularly significant in the context of ECG machines. As the electrodes detect electrical signals, the ECG machine generates heat, causing the thermal paper to undergo color changes. These color variations create the distinct tracings that healthcare professionals analyze to gain insights into the heart’s electrical activity.
Key Features of ECG Paper: Ensuring Precision and Compatibility
1. Grid Lines: ECG paper features grid lines that serve as a crucial guide for accurate measurement of time intervals and wave amplitudes. The horizontal axis measures time, while the vertical axis measures voltage. This grid structure ensures precise and standardized readings, allowing healthcare professionals to make informed assessments.
2. Paper Size and Format: Standardization for Compatibility: Standardization is a key consideration in the design of ECG paper. The paper is available in specific sizes and formats to ensure compatibility with different ECG machines. This standardization enables seamless integration with various devices used across healthcare settings, promoting consistency in recording and analysis.
ECG paper serves as a visual storyteller, capturing the differences of the heart’s electrical symphony and providing healthcare professionals with the insights needed for accurate analysis and informed decision-making in the realm of cardiac health.
Exploring Different Types of ECG Paper
In the diverse landscape of cardiac diagnostics, the choice of ECG paper becomes a nuanced decision, with considerations ranging from compatibility with specific machines to the unique requirements of various monitoring scenarios. Let’s briefly delve into the different types of ECG paper, highlighting their distinctions based on compatibility and the number of leads displayed.
Compatibility: Branded vs. Generic Compatible Paper
1. Branded Paper for Specific ECG Machines: Some ECG machines are designed to work optimally with specific branded ECG paper. For instance, Unison Bio-Med is a prominent name in the medical equipment industry, and our ECG paper is tailored to the specifications of their respective machines. Using our paper ensures seamless integration, maximizing the accuracy of tracings and minimizing the risk of compatibility issues.
2. Generic Compatible Paper: In contrast, generic compatible ECG paper is designed to work across a range of ECG machines. While not customized for a specific brand, it adheres to standardized specifications, making it versatile and suitable for use with various devices. Healthcare facilities with multiple types of ECG machines may find generic compatible paper a practical and cost-effective choice.
Number of Leads (Channels) Displayed: Standard 12-Lead vs. Specialized Paper
1. Standard 12-Lead ECGs: Standard 12-lead ECG paper is the most common type, capable of displaying the electrical activity from 12 different perspectives of the heart. This includes six limb leads and six precordial leads, providing a comprehensive overview of cardiac function. The versatility of standard 12-lead ECG paper makes it suitable for routine diagnostic purposes.
2. Specialized Paper for Holter Monitoring or Fetal ECGs: Holter monitoring and fetal ECGs present unique monitoring scenarios that require specialized papers. Holter monitoring involves continuous ECG recording over an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours. Specialized Holter paper is designed to accommodate this prolonged monitoring, ensuring accurate tracings. Fetal ECG paper, on the other hand, is tailored to the specific characteristics of fetal heart signals, catering to the unique demands of prenatal monitoring.
Emphasizing the Importance of Compatible Paper for Optimal Results
Choosing the right type of ECG paper is paramount for obtaining optimal results in cardiac diagnostics. Whether opting for branded paper tailored to specific machines or generic compatible paper for versatility, the goal is to ensure seamless integration and accuracy in recording the heart’s electrical activity. Using the appropriate paper type not only enhances the reliability of tracings but also contributes to the overall effectiveness of the diagnostic process, supporting healthcare professionals in making informed decisions for patient care.
Beyond the Basics: Features and Considerations in ECG Paper Selection
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of ECG paper, it becomes apparent that certain additional features and considerations play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of cardiac tracings. Beyond compatibility and the number of leads displayed, let’s explore aspects such as paper quality, storage recommendations, and the potential impact of environmental factors.
1. Paper Quality: Clarity for Accurate Interpretation
The quality of ECG paper is a fundamental factor that directly influences the clarity of the tracings. High-quality paper ensures that the electrical signals recorded by the ECG machine are accurately represented, allowing healthcare professionals to make precise interpretations. Clear tracings are essential for identifying subtle abnormalities and deviations in the heart’s electrical activity, leading to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans.
2. Storage Recommendations: Maintaining Optimal Paper Quality
Proper storage is paramount in preserving the integrity of ECG paper. Exposure to unfavorable conditions, such as excessive heat, humidity, or direct sunlight, can compromise the quality of the paper. It is recommended to store ECG paper in a cool, dry place and away from direct sunlight. Additionally, protecting the paper from dust and contaminants ensures that it remains in pristine condition, ready for use when needed.
3. Environmental Factors: Impact of Temperature and Humidity
Environmental factors can significantly impact the performance of ECG paper. Both temperature and humidity levels play a role in maintaining the paper’s responsiveness to the heat generated by the ECG machine. Extreme temperatures or high humidity can potentially lead to paper distortions, affecting the accuracy of tracings. Healthcare facilities should be mindful of the storage conditions and environmental factors to ensure that ECG paper retains its quality and reliability.
4. Manufacturer Specifications: Adhering to Guidelines
Each type of ECG paper may come with specific manufacturer guidelines regarding storage and environmental considerations. Healthcare professionals and facilities need to adhere to these guidelines to maintain the quality and performance of the paper. Manufacturers often provide clear instructions on the recommended storage conditions, ensuring that the paper remains in optimal condition for recording precise ECG tracings.
Healthcare professionals must be attentive to these details to ensure the reliability of ECG tracings, contributing to the overall effectiveness of cardiovascular assessments and patient care.
Selecting the Right ECG Paper: A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the right ECG paper is a critical decision that influences the accuracy of cardiac tracings and, consequently, the quality of patient care. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the process of selecting the proper ECG paper for your specific needs.
1. Compatibility with Your Specific ECG Machine Model
A. Identify Your ECG Machine Model: Start by identifying the specific make and model of your ECG machine. Different machines may have unique requirements regarding paper size, format, and responsiveness.
B. Check Manufacturer Recommendations: Refer to the recommendations provided by the manufacturer of your ECG machine. Manufacturers often specify compatible paper options to ensure optimal performance. This information can typically be found in the user manual or through the manufacturer’s website.
C. Consider Branded ECG Paper: If available, consider using ECG paper branded by the manufacturer of your ECG machine. Branded paper is designed to meet the exact specifications of the machine, ensuring seamless integration and accurate tracings.
2. Quality, Features, and Cost Considerations
A. Evaluate Paper Quality: Assess the quality of the ECG paper, considering factors such as thickness, smoothness, and the clarity of tracings. High-quality paper contributes to accurate and readable ECG recordings.
B. Explore Additional Features: Some ECG papers come with additional features, such as enhanced grid lines, perforations for easy tearing, or special coatings to resist environmental factors. Evaluate these features based on your preferences and specific requirements.
C. Balance Features and Cost: Strike a balance between desirable features and cost considerations. While advanced features may enhance user experience, it’s essential to ensure that they align with your clinical needs and budget constraints.
3. Consulting with Medical Equipment Suppliers or Manufacturers
A. Engage with Suppliers: Consult with reputable medical equipment suppliers who specialize in ECG consumables. These suppliers often have a comprehensive understanding of various paper options and can guide you in selecting the most suitable one for your ECG machine.
B. Direct Communication with Manufacturers: If necessary, directly communicate with the manufacturer of your ECG machine. Manufacturers can provide specific insights into the compatibility and recommended paper options, addressing any queries or concerns you may have.
C. Consider Manufacturer Recommendations for Consumables: Manufacturers may have a list of recommended consumables, including ECG paper, to complement their machines. Following these recommendations can contribute to optimal performance and reliability.
In conclusion, selecting the right ECG paper involves a thorough understanding of your ECG machine model, careful consideration of quality and features, and collaboration with knowledgeable suppliers or manufacturers. By following this comprehensive guide, you can make informed decisions that enhance the accuracy of ECG tracings and contribute to the overall effectiveness of cardiac diagnostics in your healthcare setting.
Beyond Recording: Interpreting ECG Tracings
Electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation stands as a skillful art mastered by medical professionals to decipher the intricate language of the heart’s electrical signals. This process goes beyond the mere recording of tracings, requiring a profound understanding of cardiac rhythms, patterns, and anomalies.
Understanding ECG Interpretation: A Professional Skill
ECG interpretation involves analyzing the patterns and shapes depicted on the ECG tracings to derive valuable insights into the heart’s condition. Skilled medical professionals, such as cardiologists, electrophysiologists, and trained healthcare providers, engage in this process to diagnose various cardiac conditions, assess overall heart health, and guide treatment decisions.
Importance of Training and Expertise: Ensuring Accuracy in Diagnosis
Accurate ECG interpretation is not an inherent skill but a learned expertise honed through rigorous training and experience. Medical professionals undergo specialized education to understand the complexities of the heart’s electrical activity, the significance of each waveform, and the potential deviations indicative of cardiac disorders. Continuous learning and staying abreast of advancements in cardiology are integral to ensuring accurate and up-to-date ECG interpretation.
Disclaimer: The Role of Qualified Healthcare Professionals
ECG interpretation is a complex and specialized skill that should be performed by qualified healthcare professionals. The information provided by ECG tracings is nuanced, and a thorough understanding of cardiac physiology, pathology, and clinical context is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
While ECGs offer invaluable information, their interpretation requires a fine understanding of various factors, including patient history, symptoms, and concurrent medical conditions. The insights gained from ECG tracings contribute significantly to the overall assessment of cardiac health, aiding in the timely detection and management of cardiovascular issues.
In summary, ECG interpretation is a vital aspect of cardiac diagnostics, unlocking the potential to unveil hidden complexities within the heart. The dedication to ongoing training and the reliance on the expertise of qualified healthcare professionals ensure that ECG interpretations lead to accurate diagnoses, ultimately contributing to enhanced patient care and well-informed medical decisions.
Troubleshooting Common ECG Paper Issues
Electrocardiogram (ECG) paper is a critical component in the process of recording and interpreting cardiac signals. However, like any technology, it may encounter issues that can affect the quality of tracings. Here’s a guide to troubleshooting common ECG paper issues:
1. Uneven or Faint Tracings
A. Possible Causes
– Insufficient pressure between the ECG electrodes and the patient’s skin.
– Poor-quality ECG paper.
– Aging or improperly stored ECG paper.
B. Troubleshooting Steps
– Ensure proper skin preparation and electrode placement.
– Check the quality of the ECG paper, and replace if necessary.
– Store ECG paper in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
2. Baseline Drift
A. Possible Causes
– Loose or inadequate electrode connections.
– Patient movement during the recording.
– Dry or aging electrodes.
B. Troubleshooting Steps
– Verify that electrodes are securely attached.
– Instruct the patient to remain still during the recording.
– If using reusable electrodes, ensure they are adequately moistened.
3. Paper Jams or Misfeeds
A. Possible Causes
– Incorrect loading of ECG paper.
– Worn-out or damaged paper feed mechanisms.
– Paper stored in high humidity conditions.
B. Troubleshooting Steps
– Reload the ECG paper carefully, following machine-specific instructions.
– Check and replace worn-out or damaged paper feed components.
– Store ECG paper in a controlled environment to prevent humidity-related issues.
4. Inconsistent Print Quality
A. Possible Causes
– Dirty or worn printing heads.
– Inadequate printer settings.
– Compatibility issues between the ECG machine and paper.
B. Troubleshooting Steps
– Clean or replace printing heads according to manufacturer guidelines.
– Adjust printer settings to optimize print quality.
– Ensure the ECG machine is compatible with the type of ECG paper being used.
5. Fading or Disappearing Tracings
A. Possible Causes
– Low-quality or incompatible thermal paper.
– Aging or exposure of paper to heat and light.
B. Troubleshooting Steps
– Use high-quality and compatible ECG paper.
– Ensure proper storage conditions, away from heat and direct sunlight.
6. Grid Misalignment
A. Possible Causes
– Incorrect loading of paper.
– Mechanical issues within the ECG machine.
B. Troubleshooting Steps
– Reload the ECG paper carefully, aligning it properly.
– If the issue persists, consult the ECG machine’s user manual or technical support.
7. ECG Paper Curling
A. Possible Causes
– Excessive humidity during storage.
– Poor-quality paper.
B. Troubleshooting Steps
– Store ECG paper in a controlled, low-humidity environment.
– Consider using high-quality, moisture-resistant paper.
Always refer to the specific user manual of your ECG machine for detailed troubleshooting instructions. If issues persist, seek assistance from the equipment manufacturer’s technical support or a qualified biomedical engineer. Regular maintenance and adherence to proper usage guidelines can prevent many common ECG paper issues, ensuring the reliability of cardiac tracings during patient assessments.
Conclusion
In summary, an ECG paper is not just a recording sheet; it’s a critical element in the diagnostic process. The quality and compatibility of ECG paper directly impact the accuracy of ECG testing. As we conclude, the call to action is clear – consult with medical equipment suppliers to ensure you have the right ECG paper for optimal patient care.
Disclaimer: The content provided serves as an informative guide and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Interpretation of ECG tracings should be performed by qualified healthcare professionals.