Welcoming a new life into the world is a remarkable journey, and ensuring the healthy growth and development of the fetus is of utmost importance.
Fetal growth monitoring plays a pivotal role in assessing the well-being of the baby and guiding medical interventions when necessary.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the significance, methods, and considerations involved in monitoring fetal growth.
Table of Contents
What is Fetal Growth Monitoring?
Fetal growth monitoring is a critical aspect of prenatal care, ensuring the well-being and development of the unborn baby throughout pregnancy.
This process involves assessing the size and development of the fetus, providing valuable insights into its overall health.
Fetal growth monitoring is an integral part of ensuring a healthy pregnancy and providing the best possible outcomes for both the expectant mother and the unborn baby.
Through advanced imaging techniques and careful assessments, healthcare professionals can track fetal growth and intervene when necessary to optimize the well-being of both the baby and the mother.
To monitor your unborn baby, you can use our Fetal Monitor UMF-8000B to monitor your baby accurately.
Methods of Fetal Growth Assessment
Fetal growth assessment is a crucial component of prenatal care, enabling healthcare professionals to monitor the development and well-being of the unborn baby. Several methods are employed to assess fetal growth accurately:
1. Ultrasound Imaging:
- Biometric Measurements: Ultrasound scans provide detailed images of the fetus, allowing for accurate measurements of key parameters such as head circumference, abdominal circumference, and femur length.
- Visualizing Organs: Ultrasound helps visualize internal structures, organs, and the placenta, offering insights into the overall health and development of the fetus.
2. Fundal Height Measurement:
- External Measurement: Fundal height is measured externally by assessing the distance from the top of the uterus to the pubic bone.
- Estimating Uterine Size: This method provides a quick assessment of uterine size, helping estimate fetal growth and ensuring it aligns with the expected progression.
3. Doppler Blood Flow Studies:
- Assessing Blood Flow: Doppler ultrasound studies evaluate blood flow in the umbilical cord and fetal vessels, providing information about placental function and fetal well-being.
- Detection of Abnormalities: Changes in blood flow patterns can indicate potential issues, prompting further investigation.
4. Serial Ultrasonography:
- Continuous Monitoring: Serial ultrasonography involves repeated ultrasound scans at regular intervals to monitor fetal growth throughout pregnancy.
- Dynamic Assessment: This method allows healthcare providers to track changes in biometric measurements, identifying trends or deviations from expected growth patterns.
5. Customized Growth Charts:
- Individualized Assessments: Customized growth charts take into account various factors such as maternal characteristics, ethnicity, and previous pregnancy history.
- Personalized Analysis: This approach provides a more personalized assessment, considering the unique circumstances of each pregnancy.
6. Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP) Testing:
- Screening for Neural Tube Defects: MSAFP testing measures the levels of alpha-fetoprotein in the mother’s blood, helping screen for neural tube defects and certain chromosomal abnormalities.
- Indirect Indicator of Fetal Well-Being: While not a direct measure of fetal growth, abnormal MSAFP levels may prompt further investigation into fetal health.
7. Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) Measurement:
- Assessing Amniotic Fluid Levels: AFI measurement evaluates the volume of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus.
- Indication of Fetal Well-Being: Abnormalities in amniotic fluid levels can be associated with fetal growth restriction or other complications.
8. Placental Grading:
- Evaluating Placental Maturity: Grading the placenta through ultrasound helps assess its maturity and functioning.
- Understanding Fetal Nutrient Supply: The placental grade provides information about the efficiency of nutrient and oxygen supply to the fetus.
9. Biophysical Profile (BPP):
- Combination of Assessments: BPP combines ultrasound assessments (fetal movement, muscle tone, breathing, amniotic fluid levels) to evaluate overall fetal well-being.
- Scoring System: Each component is scored, and the cumulative score guides decisions about ongoing monitoring or potential interventions.
Fetal growth assessment utilizes a combination of these methods, allowing healthcare providers to comprehensively evaluate fetal development, detect potential issues, and provide timely interventions when necessary.
The integration of advanced imaging techniques and non-invasive tests enhances the accuracy of assessing the health and growth of the unborn baby throughout pregnancy.
Significance of Fetal Biometry
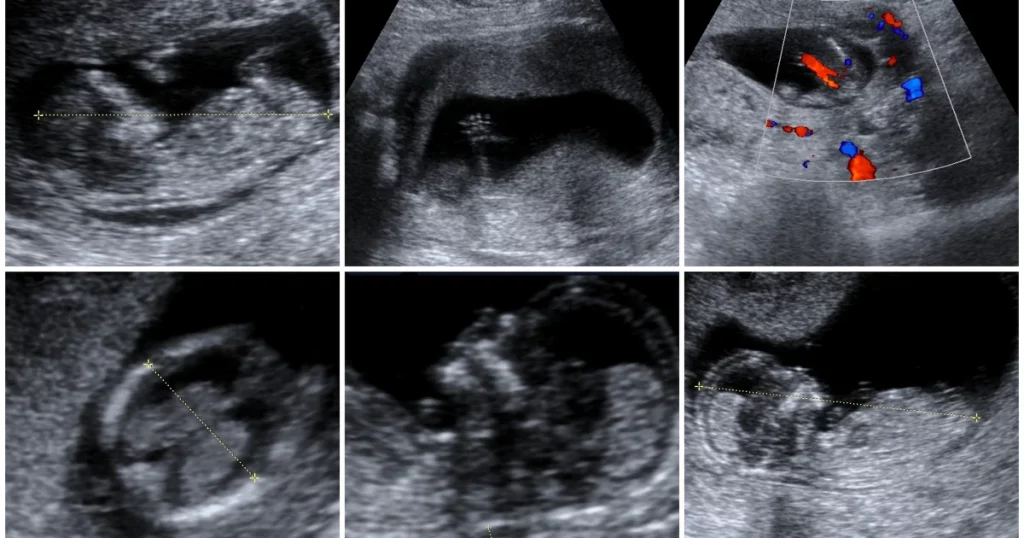
Fetal biometry, a branch of prenatal ultrasound, holds immense significance in obstetric care by providing detailed measurements of various fetal structures.
This quantitative approach aids healthcare professionals in assessing the growth, development, and overall well-being of the unborn baby.
Here’s a closer look at the significance of fetal biometry:
1. Accurate Dating of Pregnancy:
- Crown-Rump Length (CRL): Early in pregnancy, measuring the CRL helps accurately determine gestational age, enabling precise dating of the pregnancy.
- Establishing a Baseline: Accurate dating is crucial for establishing a baseline for fetal growth assessment throughout the different trimesters.
2. Monitoring Fetal Growth:
- Biometric Parameters: Fetal biometry involves measuring key parameters such as head circumference, abdominal circumference, and femur length.
- Identification of Growth Abnormalities: Deviations from expected growth patterns can indicate potential issues, including fetal growth restriction or macrosomia.
3. Assessment of Fetal Well-Being:
- Amniotic Fluid Levels: Biometric measurements, along with assessing amniotic fluid levels, contribute to the overall evaluation of fetal well-being.
- Dynamic Indicators: Changes in fetal biometry parameters over time provide dynamic insights into the health and development of the fetus.
4. Identification of Structural Anomalies:
- Detailed Anatomical Assessment: Fetal biometry allows for a detailed examination of various fetal structures, aiding in the identification of potential structural anomalies.
- Early Intervention: Early detection of anomalies supports timely intervention and management strategies.
5. Monitoring Multiple Pregnancies:
- Growth Discrepancies: In the case of multiple pregnancies, fetal biometry helps monitor growth discrepancies between twins or other multiples.
- Tailoring Care Plans: Tailoring care plans based on individual growth patterns is crucial for optimizing outcomes in multiple gestations.
6. Evaluation of Placental Function:
- Umbilical Artery Doppler: Combining fetal biometry with Doppler studies assesses placental function, ensuring an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus.
- Detection of Complications: Abnormal Doppler findings may indicate issues such as placental insufficiency, guiding further investigations.
7. Facilitating Informed Decision-Making:
- Patient Counseling: Fetal biometry results provide valuable information for patient counseling, allowing expectant parents to make informed decisions regarding the pregnancy.
- Communication with Healthcare Providers: Understanding the significance of biometric measurements fosters open communication between healthcare providers and patients.
8. Guiding Timing of Interventions:
- Timing of Delivery: In cases of identified growth abnormalities or other complications, fetal biometry assists in determining the optimal timing for interventions such as induction of labor or cesarean section.
- Minimizing Risks: Timely interventions based on accurate biometric data contribute to minimizing risks and optimizing maternal and fetal outcomes.
9. Research and Clinical Studies:
- Data for Research: Fetal biometry contributes to the collection of standardized data for research studies and clinical trials.
- Advancing Obstetric Knowledge: The aggregation of biometric information enhances obstetric knowledge, contributing to ongoing improvements in prenatal care.
In summary, fetal biometry plays a pivotal role in modern obstetrics, providing a comprehensive toolkit for assessing fetal growth, well-being, and structural integrity.
The precise measurements obtained through biometric assessments empower healthcare professionals to make informed decisions, offer timely interventions, and support expectant parents throughout the pregnancy journey.
Tracking Fetal Growth Percentiles
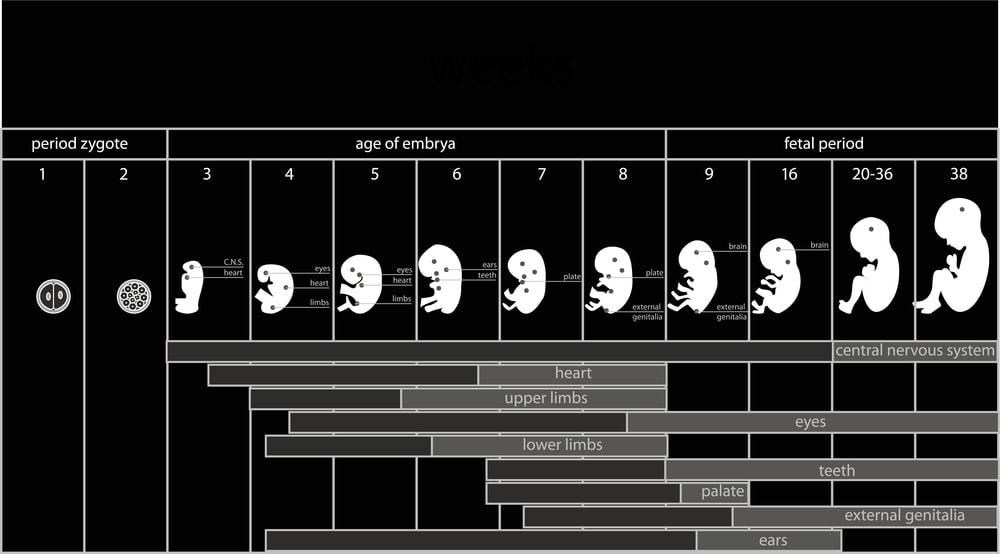
Read about: Fetal Development – How to Calculate Gestational Age
Monitoring fetal growth is a critical aspect of prenatal care, and the use of fetal growth percentiles is an invaluable tool for assessing a baby’s development in the womb.
Fetal growth percentiles compare an individual fetus’s measurements to a standardized population, allowing healthcare providers to evaluate whether the baby’s growth falls within expected ranges.
Here’s a closer look at the significance of tracking fetal growth percentiles:
1. Individualized Assessment:
- Fetal growth percentiles provide an individualized assessment of a baby’s size based on factors such as gestational age, sex, and maternal characteristics.
- This approach recognizes that each pregnancy is unique, considering various factors that can influence fetal growth.
2. Early Detection of Abnormalities:
- Deviations from the expected fetal growth percentiles may indicate potential issues such as fetal growth restriction or macrosomia.
- Early identification of growth abnormalities enables timely interventions and management strategies to optimize outcomes.
3. Gestational Age Consideration:
- Fetal growth percentiles take into account the gestational age of the fetus, acknowledging that normal growth varies at different stages of pregnancy.
- This consideration ensures a more accurate assessment, avoiding inappropriate comparisons between fetuses at different developmental stages.
4. Sex-Specific Assessment:
- Recognizing the inherent differences in growth patterns between male and female fetuses, growth percentiles are often stratified by sex.
- This sex-specific approach enhances the precision of growth assessments, providing a more nuanced understanding of fetal development.
5. Maternal Characteristics:
- Maternal factors such as height, weight, and ethnicity can influence fetal growth. Fetal growth percentiles may adjust for these maternal characteristics.
- This adjustment helps account for variations in growth influenced by the diverse backgrounds and physical characteristics of expectant mothers.
6. Dynamic Monitoring Over Time:
- Fetal growth percentiles allow for dynamic monitoring of a baby’s growth trajectory throughout the pregnancy.
- Regular assessments at different time points offer insights into whether the fetus is maintaining a consistent growth pattern or deviating from the expected path.
7. Prevention of Adverse Outcomes:
- Tracking fetal growth percentiles facilitates the early detection of factors that may lead to adverse outcomes, such as preterm birth or complications during labor.
- Proactive measures can be taken to address identified issues, minimizing risks and optimizing maternal and fetal health.
8. Research and Data Collection:
- Aggregated data from fetal growth percentiles contribute to ongoing research in obstetrics and perinatology.
- The information gathered helps advance medical knowledge, refine growth standards, and improve the accuracy of prenatal care practices.
Tracking fetal growth percentiles is a valuable strategy in prenatal care, offering a comprehensive and nuanced approach to assessing the well-being and development of the unborn baby.
This individualized and dynamic method of monitoring contributes to the provision of optimal care, supporting healthy pregnancies and positive outcomes for both mothers and their babies.
Role of Doppler Ultrasound in Fetal Monitoring
Doppler ultrasound has revolutionized the field of obstetrics by offering a non-invasive and dynamic method for assessing fetal well-being during pregnancy.
This advanced imaging technique utilizes sound waves to evaluate blood flow, providing valuable insights into the circulatory system of both the fetus and the placenta.
Here’s a detailed look at the pivotal role Doppler ultrasound plays in fetal monitoring:
1. Non-Invasive Blood Flow Assessment
- Doppler ultrasound measures the velocity of blood flow in vessels without the need for invasive procedures.
- This non-invasive nature allows healthcare providers to gather critical information about fetal and placental circulation without posing risks to the mother or the unborn baby.
2. Uterine and Umbilical Artery Evaluation
- Doppler ultrasound assesses blood flow in the uterine and umbilical arteries, offering insights into the adequacy of oxygen and nutrient supply to the fetus.
- Abnormalities in these blood vessels may indicate conditions such as placental insufficiency, growth restriction, or other complications affecting fetal well-being.
3. Detection of Fetal Anomalies:
- Doppler ultrasound aids in detecting anomalies or irregularities in blood flow patterns within fetal organs.
- Identification of abnormalities, such as cardiac defects, helps healthcare providers plan appropriate interventions or treatments for the baby’s well-being.
4. Assessment of Fetal Heart Rate:
- Doppler ultrasound allows for the assessment of the fetal heart rate, a crucial parameter in monitoring fetal health.
- Changes in heart rate patterns may indicate distress or other cardiac issues, prompting further investigation and timely interventions.
5. Monitoring Twin Pregnancies:
- Doppler ultrasound is particularly valuable in monitoring twin pregnancies, where the risk of complications is higher.
- The technique helps assess blood flow in each twin individually, providing critical information for managing the unique challenges associated with multiple pregnancies.
6. Evaluation of Placental Function:
- Doppler ultrasound provides a means to evaluate placental function by assessing blood flow in the placental vessels.
- Abnormalities in placental blood flow may be indicative of placental insufficiency, a condition that can impact fetal growth and development.
7. Risk Stratification in High-Risk Pregnancies:
- High-risk pregnancies, such as those with pre-existing conditions or a history of complications, benefit from Doppler ultrasound for risk stratification.
- Early identification of potential issues allows for proactive management and personalized care plans tailored to the specific needs of each pregnancy.
8. Guidance for Timing of Delivery:
- Doppler ultrasound findings contribute to decision-making regarding the timing of delivery in high-risk pregnancies.
- Monitoring blood flow dynamics helps healthcare providers determine the optimal gestational age for delivery, balancing the risks of preterm birth and complications.
9. Reduction of Unnecessary Interventions:
- Doppler ultrasound results aid in avoiding unnecessary interventions in pregnancies where blood flow and fetal well-being are within normal ranges.
- This precision in monitoring helps reduce the risk of iatrogenic complications and ensures a judicious approach to medical interventions.
Doppler ultrasound has emerged as an indispensable tool in the realm of fetal monitoring, offering a wealth of information that guides clinical decision-making and enhances the overall management of pregnancy.
Its ability to assess blood flow dynamics, detect anomalies, and stratify risks makes it an essential component of modern obstetric care, contributing to improved outcomes for both mothers and their babies.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring during pregnancy is a fundamental aspect of prenatal care, aiming to ensure the well-being of both the expectant mother and the developing fetus.
This ongoing process involves a series of assessments, screenings, and examinations conducted at various stages of pregnancy.
The importance of regular monitoring extends beyond simple observation; it plays a crucial role in identifying and addressing potential issues, promoting optimal maternal and fetal health, and facilitating informed decision-making.
Here are key aspects highlighting the significance of regular monitoring during pregnancy:
1. Early Detection of Complications:
- Regular check-ups enable healthcare providers to detect potential complications early in pregnancy.
- Timely identification of issues such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or fetal abnormalities allows for prompt intervention and management.
2. Assessment of Fetal Growth and Development:
- Monitoring includes measurements and assessments to track fetal growth and development.
- This helps ensure that the baby is progressing appropriately, and any deviations from the expected growth pattern can be addressed proactively.
3. Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar Management:
- Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to manage and monitor maternal blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
- Control of these parameters is essential for preventing complications like hypertension or gestational diabetes that can impact both maternal and fetal health.
4. Screening for Genetic and Congenital Anomalies:
- Regular prenatal visits include screenings and tests to assess the risk of genetic or congenital anomalies.
- Early detection enables parents to make informed decisions about their pregnancy and prepare for potential challenges.
5. Guidance on Nutrition and Lifestyle:
- Monitoring provides an opportunity for healthcare providers to offer guidance on nutrition, lifestyle, and prenatal care.
- Expectant mothers receive personalized advice to support their well-being and promote a healthy pregnancy.
6. Emotional and Psychological Support:
- Regular visits create a platform for expectant parents to discuss their emotional well-being and address any concerns or anxieties.
- Emotional support is a vital component of prenatal care, contributing to a positive pregnancy experience.
7. Preparation for Labor and Delivery:
- Regular monitoring includes discussions about labor and delivery preferences, birthing plans, and options for pain management.
- This preparation empowers expectant parents with knowledge and helps reduce anxiety about the upcoming delivery.
8. Monitoring High-Risk Pregnancies:
- For pregnancies considered high-risk due to maternal age, pre-existing conditions, or other factors, regular monitoring is especially critical.
- Close surveillance allows for early intervention and specialized care to optimize outcomes.
9. Prevention and Management of Anemia:
- Regular blood tests during pregnancy help monitor hemoglobin levels, preventing and addressing anemia.
- Adequate management of iron deficiency contributes to maternal health and prevents complications.
10. Optimizing Birth Planning:
- Regular monitoring assists in creating a birth plan that aligns with the preferences and needs of expectant parents.
- This includes decisions about the birthing environment, pain relief options, and the involvement of support persons.
11. Postpartum Planning and Support:
- Prenatal visits often include discussions about postpartum care, breastfeeding, and the emotional adjustments after childbirth.
- Preparing expectant parents for the postpartum period contributes to a smoother transition into parenthood.
In essence, regular monitoring during pregnancy is a comprehensive and proactive approach to maternal and fetal care.
It serves as a foundation for healthy pregnancies, allowing healthcare providers to tailor interventions, provide support, and empower expectant parents with the knowledge needed for a positive pregnancy and childbirth experience.
Addressing Growth Restriction Concerns
Growth restriction, also known as intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), refers to a condition where a fetus does not achieve the expected growth potential during pregnancy.
This situation raises concerns about the well-being of both the fetus and the expectant mother.
Addressing growth restriction concerns involves a comprehensive approach aimed at identifying underlying causes, monitoring fetal well-being, and implementing interventions to optimize outcomes.
Here are key aspects of addressing growth restriction concerns during pregnancy:
1. Early Detection Through Prenatal Monitoring:
- Routine prenatal check-ups include assessments of fetal growth through measurements like fundal height and ultrasound examinations.
- Early detection of growth restriction allows for timely interventions to address underlying factors and enhance fetal well-being.
2. Identifying Underlying Causes:
- Healthcare providers conduct thorough evaluations to identify potential causes of growth restriction.
- Factors such as maternal health conditions, placental issues, genetic factors, or certain infections may contribute to growth restriction.
3. Detailed Ultrasound Examinations:
- Advanced ultrasound techniques, including Doppler studies, help evaluate blood flow to the placenta and assess fetal well-being.
- Detailed examinations aid in understanding the specific aspects of growth restriction, guiding appropriate management.
4. Monitoring Fetal Well-Being:
- Regular monitoring of fetal heart rate and movement provides insights into the well-being of the growth-restricted fetus.
- Non-stress tests (NST) and biophysical profiles (BPP) are common assessments to gauge fetal health and responsiveness.
5. Nutritional Support and Lifestyle Modifications:
- Nutritional counseling ensures that the expectant mother receives adequate nutrients crucial for fetal growth.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding smoking and alcohol, contribute to a healthier environment for fetal development.
6. Management of Underlying Health Conditions:
- Addressing maternal health conditions, such as hypertension or diabetes, is essential to improve fetal growth.
- Collaborative care involving obstetricians, maternal-fetal medicine specialists, and other healthcare professionals optimizes management.
7. Timing and Mode of Delivery Considerations:
- The timing and mode of delivery are carefully considered based on the severity of growth restriction and gestational age.
- In some cases, early delivery may be recommended to mitigate risks associated with continued intrauterine growth restriction.
8. Close Collaboration Between Specialists:
- Growth-restricted pregnancies often require a multidisciplinary approach involving obstetricians, neonatologists, and other specialists.
- Collaborative care ensures comprehensive management and coordination of interventions.
9. Steroid Administration for Fetal Lung Maturity:
- In cases where preterm delivery is anticipated, administering steroids helps enhance fetal lung maturity.
- This intervention is crucial for improving the outcomes of premature infants.
10. Postpartum Follow-Up and Neonatal Care:
- Postpartum care involves monitoring both the mother’s recovery and the newborn’s health.
- Neonatal care, including specialized care for preterm infants, is essential for optimizing outcomes after delivery.
Addressing growth restriction concerns requires a tailored and vigilant approach to prenatal care.
Through early detection, collaborative management, and ongoing monitoring, healthcare providers aim to optimize fetal well-being and navigate potential challenges associated with growth restriction.
The goal is to support the best possible outcomes for both the expectant mother and the newborn.
Final Words
In nurturing life through comprehensive fetal growth monitoring, healthcare professionals weave together the art and science of obstetric care.
This guide serves as a roadmap for expectant parents and healthcare providers, fostering a collaborative approach to ensuring the well-being of both mother and baby.
Embracing the journey of pregnancy with knowledge and proactive care sets the stage for a healthy start to the miracle of life.