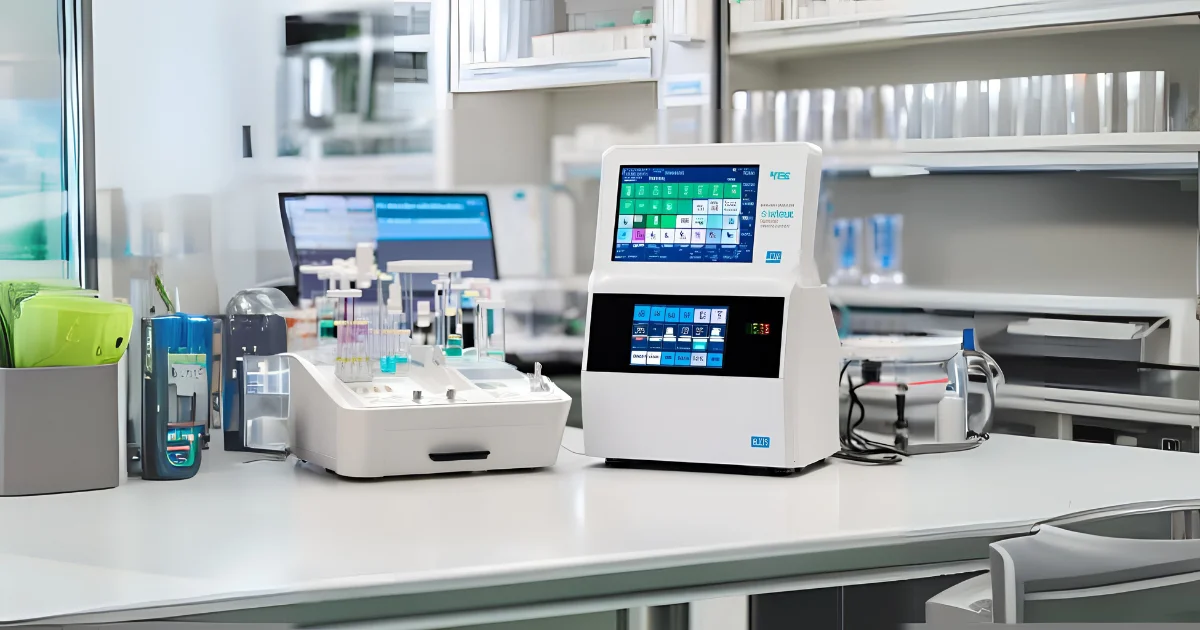
Did you know that over 70% of clinical decisions in hospitals depend on laboratory test results? From diagnosing infections to managing chronic diseases, lab-based diagnostics are the backbone of modern medicine — and at the heart of these processes lies in vitro diagnostics (IVD).
Simply put, in vitro diagnostics refer to medical tests performed outside the human body (“in vitro” means “in glass”) to detect diseases, monitor health conditions, or guide treatment decisions. Instead of testing inside the body, as in imaging or physical exams, IVD involves analyzing samples like blood, urine, or tissue using specialized equipment and reagents.
You encounter IVD applications more often than you might think. Common in vitro diagnostics examples include:
- Pregnancy test kits, which detect hormone levels in urine
- Blood glucose monitors, essential for diabetes management
- Electrolyte analysis, used to assess vital ions like sodium and potassium in patient blood samples
- Hematology tests, such as complete blood counts, performed with automated cell counters
Together, these tools form the foundation of laboratory medicine, enabling clinicians to make fast, evidence-based decisions that can save lives.
In short, IVD (In Vitro Diagnostics) is not just another medical term — it’s the unseen force driving accurate diagnosis and personalized care in hospitals and clinics worldwide.
Table of Contents
Why In Vitro Diagnostics Matter in Modern Medicine
In modern healthcare, speed and accuracy in diagnosis can mean the difference between early recovery and delayed treatment. That’s where in vitro diagnostics (IVD) play a crucial role. These tests allow medical professionals to detect diseases at an early stage, monitor patients’ progress, and tailor treatments based on precise laboratory findings.
In fact, more than 70% of all clinical decisions are based on IVD test results, according to industry reports. This means that doctors, nurses, and specialists rely heavily on laboratory data to confirm diagnoses, adjust medications, and evaluate the effectiveness of therapies.
By providing reliable, measurable, and timely information, IVD systems help healthcare providers:
- Detect diseases early, even before symptoms appear — allowing for preventive interventions.
- Monitor ongoing conditions, such as diabetes, electrolyte imbalances, or blood disorders, ensuring patients receive consistent care.
- Improve treatment accuracy, since lab-based data supports evidence-driven medical decisions.
In hospitals and clinics, every test result counts — and IVD tools make that possible. From routine blood work to complex molecular analysis, they form the diagnostic foundation that guides patient care, supports clinicians, and ultimately improves treatment outcomes.
Types and Examples of In Vitro Diagnostic Products
Let’s be honest — the world of in vitro diagnostics can sound a bit intimidating at first. It’s full of technical terms and complex devices that seem like they belong in a sci-fi lab. But once you break it down, it’s actually pretty fascinating. Every blood test, every pregnancy strip, every analyzer — they all work together behind the scenes to help doctors make accurate, life-saving decisions.
So, let’s take a closer look at the main types of in vitro diagnostic products and how they fit together like puzzle pieces in modern healthcare.
1. Test Kits: The Everyday Heroes
Think of in vitro diagnostic test kits as the “first responders” of the medical world. They’re quick, reliable, and designed for everyday use — both in hospitals and at home.
Common examples?
- Pregnancy test kits that detect hCG hormones in urine.
- Rapid antigen kits for infections like COVID-19.
- Blood glucose meters used by millions of diabetics every day.
These kits give fast answers, helping patients and clinicians make immediate decisions. No waiting, no guessing — just clear results when time really matters.
2. Reagents: The Invisible Powerhouses
Now, here’s something most people never think about — the chemicals that actually make testing possible. These are called reagents, and they’re the secret ingredients behind accurate results.
Without reagents, analyzers and test kits are just fancy boxes. Reagents react with the patient’s sample (like blood or urine) to reveal what’s inside — glucose levels, electrolytes, cell counts, and so on.
You can think of them as the “truth serum” in diagnostics — they reveal what’s really happening inside your body!
3. Analyzers: The Brains Behind the Operation
When it comes to serious testing, analyzers are where the magic happens. These in vitro diagnostics medical devices are high-precision instruments that automate complex tests in hospitals and laboratories.
For example:
- Cell counters (like those from Unison Bio-Med) analyze blood samples to measure red and white blood cell counts, helping detect infections, anemia, or immune disorders.
- Electrolyte analyzers measure sodium, potassium, and chloride levels — critical indicators for hydration, kidney, and heart function.
These analyzers don’t just save time; they reduce human error and ensure every test result is accurate and consistent. And for busy hospital labs, that’s priceless.
4. Diagnostic Devices: The Complete System
Finally, we have diagnostic devices — the complete systems that bring everything together. Imagine a smooth workflow where test kits, reagents, and analyzers all talk to each other seamlessly. That’s what modern IVD systems do.
These integrated setups handle everything — from sample preparation to automated data reporting — giving doctors instant insights into a patient’s condition. According to a 2024 healthcare technology report, automated IVD systems can improve lab efficiency by up to 40% and reduce reporting errors by 30%. That means faster, more confident medical decisions.
Bringing It All Together
Here’s the big picture: Each part of the in vitro diagnostics ecosystem plays a unique role. Test kits provide quick answers, reagents make results possible, analyzers perform the complex work, and diagnostic devices connect it all together.
So next time you hear about a “lab test,” remember — it’s not just a machine or a strip. It’s a carefully orchestrated system built to protect and preserve life. And at Unison Bio-Med, we’re proud to be part of that system — delivering reliable analyzers that help hospitals and clinics provide faster, more accurate care, every single day.
Key Applications of In-Vitro Diagnostics
1. Infectious Disease Detection
- Role: Identifies pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and fungi through molecular or immunoassay-based testing.
- Examples:
- PCR tests for COVID-19 detection.
- ELISA tests for HIV and hepatitis.
- Impact: Enables rapid containment of outbreaks and targeted treatments.
2. Cancer Diagnostics
- Role: Detects cancer biomarkers in blood or tissue samples.
- Examples:
- Liquid biopsies to detect circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA).
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC) tests for hormone receptor status in breast cancer.
- Impact: Facilitates early-stage detection and personalized oncology treatments.
3. Genetic and Genomic Testing
- Role: Analyzes DNA or RNA to identify genetic mutations, hereditary conditions, or disease predisposition.
- Examples:
- BRCA testing for breast and ovarian cancer risk.
- Newborn genetic screening.
- Impact: Empowers proactive healthcare decisions and family planning.
4. Chronic Disease Management
- Role: Monitors biomarkers for conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders.
- Examples:
- HbA1c tests for diabetes management.
- Lipid panels for cholesterol and cardiovascular risk assessment.
- Impact: Supports ongoing disease management and prevention strategies.
5. Precision Medicine
- Role: Provides actionable insights to guide personalized therapies.
- Examples:
- Pharmacogenomic tests to determine drug efficacy and safety for individuals.
- Biomarker analysis to identify optimal cancer immunotherapy candidates.
- Impact: Reduces trial-and-error prescribing and enhances treatment outcomes.
How Automated Analyzers Transform Diagnostic Accuracy
If you’ve ever worked in a hospital lab, you know the pressure — dozens of samples arrive every hour, doctors are waiting on results, and accuracy can’t be compromised for even a second. In that environment, automated analyzers aren’t just helpful — they’re absolutely essential.
These powerful in vitro diagnostics devices do what no human can: process hundreds of tests in minutes, with precision down to the smallest decimal. They’ve redefined how medical laboratories operate — bringing speed, accuracy, and reliability to a level that was once unimaginable.
From Manual Errors to Machine Precision
Once upon a time, lab technicians had to manually mix reagents, count cells under a microscope, and record results by hand. It was slow, exhausting, and — let’s face it — left plenty of room for human error.
Now, advanced analyzers like automated cell counters and electrolyte analyzers handle all that work in seconds. They not only reduce the chance of mistakes but also ensure every test result is consistent — whether it’s the first sample of the day or the hundredth.
According to recent clinical studies, automated analyzers improve diagnostic accuracy by up to 25% compared to manual testing methods. That’s not just a number — it’s a life-saving difference for patients relying on precise results.
Cell Counters: The Foundation of Hematology Testing
Let’s start with cell counters, one of the most indispensable tools in the diagnostic lab. These devices perform complete blood counts (CBCs) — analyzing red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin levels.
Why does this matter?
Because the results help doctors detect anemia, infections, immune system issues, and even some cancers — often before symptoms become obvious.
At Unison Bio-Med, our cell counters are engineered for speed, consistency, and accuracy, giving labs confidence in every report they produce. When a single reading can influence a life-saving treatment plan, precision isn’t optional — it’s everything.
Electrolyte Analyzers: Small Tests, Big Impact
Now, let’s talk about another unsung hero — the electrolyte analyzer. It might not sound glamorous, but it’s one of the most critical devices in clinical chemistry. These analyzers measure key electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride — the substances that keep your body’s cells functioning and your heart beating properly.
Even slight imbalances can cause serious complications. That’s why reliable, fast electrolyte testing is essential in intensive care units, emergency rooms, and general hospital labs.
Unison Bio-Med’s electrolyte analyzers are designed to deliver quick, accurate results — helping clinicians make informed, real-time decisions about hydration therapy, kidney function, and critical care treatment.
Faster Results, Better Care
Automated IVD analyzers don’t just save time — they save lives. Faster test turnaround means quicker diagnosis, earlier treatment, and improved patient outcomes. For healthcare professionals, it means peace of mind knowing they can trust the numbers they see.
And for hospitals and clinics, investing in high-quality analyzers isn’t just about efficiency — it’s about building a reputation for reliability, accuracy, and patient-centered care.
At Unison Bio-Med, we believe innovation in diagnostics starts with trust. Our advanced analyzers are built to empower healthcare professionals — giving them the precision they need, when they need it most.
Benefits of In-Vitro Diagnostics

1. Enhanced Patient Outcomes: Early and accurate detection leads to timely interventions.
2. Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces healthcare costs by preventing advanced disease stages and hospitalizations.
3. Rapid Turnaround Times: Point-of-care and molecular testing deliver results within minutes to hours.
4. Public Health Preparedness: Essential for managing pandemics, outbreaks, and community health programs.
5. Innovation in Personalized Medicine: Aligns treatments with patients’ genetic and molecular profiles.
Challenges Facing In-Vitro Diagnostics
1. High Costs of Advanced Technologies: Barriers for widespread adoption in low-resource settings.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles: Time-intensive processes for obtaining approvals and maintaining quality standards.
3. Data Management and Integration: Ensuring interoperability across electronic health records (EHRs) and diagnostic platforms.
4. Skilled Workforce Shortages: Requires trained professionals to operate complex diagnostic tools.
Real-World Applications in Hospitals and Clinics
Step into any busy hospital laboratory, and you’ll see it — the quiet hum of analyzers working behind the scenes while doctors, nurses, and lab techs move with precision and urgency. Every beep, every printout, every vial tells a story — a patient waiting for answers. That’s the true heartbeat of in vitro diagnostics in action.
These diagnostic systems don’t just sit in sterile labs; they’re woven into the daily rhythm of healthcare. From emergency rooms to specialized departments, automated analyzers like cell counters and electrolyte analyzers are the silent partners helping clinicians make faster, more accurate medical decisions.
Emergency and Critical Care Units
When every second counts — like in cardiac arrest or dehydration cases — electrolyte analyzers are indispensable. They quickly measure sodium, potassium, and chloride levels to guide fluid and medication therapy.
Imagine an ICU nurse waiting for lab results before adjusting an IV drip — that few-minute delay could mean everything. Fast, accurate electrolyte testing saves those minutes.
Unison Bio-Med’s analyzers deliver reliable results in record time, helping hospitals act fast and confidently.
Clinical Laboratories and Pathology Departments
In clinical labs, precision is the name of the game. Cell counters provide detailed blood analysis — a critical part of diagnosing anemia, infections, and blood cancers. A complete blood count (CBC) is often the first step in nearly every diagnostic process.
With Unison Bio-Med’s advanced cell counters, labs can process high volumes of samples quickly without compromising accuracy. That means shorter waiting times for patients and smoother workflow for technicians who already juggle hundreds of tests daily.
Outpatient Clinics and Diagnostic Centers
Not all testing happens inside big hospitals. Smaller diagnostic centers and private clinics depend on compact, easy-to-use IVD equipment that still delivers professional-grade results.
Whether it’s a routine blood test or an electrolyte panel for a diabetic patient, these centers need reliable machines that work perfectly day in and day out.
That’s where Unison Bio-Med stands out — offering high-performance diagnostic devices tailored to both large medical institutions and smaller, fast-paced clinics.
Building Trust Through Reliable Diagnostics
Beyond speed and precision, there’s something even more valuable that IVD systems create — trust.
When doctors know their lab results are accurate, they make bolder, more confident decisions.
When patients see consistent reports, they feel safer and more informed about their health.
Reliable in vitro diagnostics don’t just improve outcomes — they strengthen the relationship between caregivers and patients. And that’s the kind of impact Unison Bio-Med is proud to support every single day.
Choosing the Right In Vitro Diagnostic Equipment
When it comes to investing in in vitro diagnostic (IVD) equipment, hospitals and clinics can’t afford to get it wrong. The right analyzer isn’t just a machine — it’s the foundation of diagnostic accuracy, patient safety, and workflow efficiency. But with so many options on the market, how do you know which one truly fits your needs?
Let’s break it down in simple, practical terms.
1. Accuracy Comes First — Always
It doesn’t matter how fast a device is if the results aren’t accurate.
A study published in Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine found that even a 1% error in laboratory data can lead to incorrect clinical decisions. That’s why top-tier in vitro diagnostics products focus on precision as their first priority.
Unison Bio-Med’s analyzers are calibrated for dependable performance, ensuring every blood count or electrolyte reading is consistent, reproducible, and clinically valid. When your patients’ health depends on the data, there’s no room for “almost right.”
2. Speed and Efficiency Save Lives
In emergency or critical care, time is more than valuable — it’s life-saving.
That’s why choosing equipment that processes results quickly and automatically is essential. Automated cell counters and electrolyte analyzers streamline the workflow, allowing labs to handle more samples in less time without compromising accuracy.
Hospitals that upgrade to automated systems report 30–40% faster test turnaround times, according to healthcare efficiency reports. That’s time that can literally change patient outcomes.
3. Ease of Use and Maintenance
You shouldn’t need an engineering degree to run your analyzer. The best in vitro diagnostics medical devices are designed with user-friendly interfaces, minimal manual handling, and easy maintenance.
Unison Bio-Med focuses on intuitive design and reliable performance — so even under pressure, your lab staff can work confidently without constant recalibration or downtime.
4. After-Sales Support and Service
This is a big one — and often overlooked. Buying an analyzer isn’t a one-time transaction; it’s a long-term partnership. Reliable technical support, spare parts availability, and timely maintenance services make all the difference.
Unison Bio-Med stands beside its clients long after installation — with dedicated support teams, training assistance, and prompt servicing to keep your devices running smoothly. Because in healthcare, interruptions aren’t an option.
5. Compliance and Quality Assurance
Always choose devices that meet international quality standards and regulatory requirements.
Certified IVD medical devices not only guarantee safety and performance but also build credibility with patients and healthcare partners.
Unison Bio-Med’s analyzers are developed with strict adherence to quality benchmarks — ensuring every product aligns with clinical standards and institutional needs.
Choosing the right in vitro diagnostic equipment isn’t just a technical decision — it’s a strategic one. It determines how efficiently your lab runs, how accurate your results are, and ultimately, how confidently your medical team can care for patients.
When you partner with Unison Bio-Med, you’re not just buying equipment; you’re investing in precision, trust, and performance that empower better healthcare every day.
Conclusion
In-vitro diagnostics are redefining the boundaries of disease detection and patient care. By embracing advancements in technology, integrating data-driven insights, and ensuring accessibility, IVD is paving the way for a healthier, more informed future.
Take Action Today! Explore our cutting-edge IVD solutions and learn how they can revolutionize your diagnostic capabilities. Contact us for more information.